ElasticSearch 7.6 学习笔记
分词器
分词器概述
分词器包含三部分
- character filter: 分词之前的预处理,过滤掉HTML标签,特殊符号转换等。
- tokenizer: 分词
- token filter: 标准化,大小写,同义词,单复数转换。
分词器的类别
keyword: 不对输入做任何的处理,直接将输入当做一个 term 输出standard: 对英文按 word 分词,对中文按照汉字分词- …
创建 & 使用分词器
下面为创建索引时指定类型的设置:
为索引创建了 person 类型,其中包含 user 字段
{
"mappings": {
"person": {
"properties": {
"user": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
}
}
}
}
- search_analyzer 是搜索词的分词器
- analyzer 是字段文本的分词器
分词器的使用示例
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "keyword",
"text": "Mastering ElasticSearch, elasticsearch in action"
}
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "Mastering ElasticSearch, elasticsearch in action",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 48,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
}
]
}
---
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "icu_analyzer",
"text": "他说的确实在理"
}
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "他",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "说的",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "确实",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "在",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "理",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
GET /_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "他说的确实在理"
}
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "他",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 1,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "说",
"start_offset" : 1,
"end_offset" : 2,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "的",
"start_offset" : 2,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "确",
"start_offset" : 3,
"end_offset" : 4,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "实",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 5,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "在",
"start_offset" : 5,
"end_offset" : 6,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 5
},
{
"token" : "理",
"start_offset" : 6,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<IDEOGRAPHIC>",
"position" : 6
}
]
}
聚合分析
- Bucket Aggregation
将一些列满足特定条件的文档聚合成一个桶
- Metric Aggreation
一些数学运算,可以对文档的字段进行统计分析
# 根据电影的年份进行分组
GET movies/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"movie_year": {
"terms": {
"field": "year"
}
}
}
}
# 将电影根据年份分组后,再来求每组内的最大年份和最小年份(由于text 类型不能比较,只好求个最大年份)
GET movies/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"movie_year": {
"terms": {
"field": "year"
},
"aggs": {
"max_year": {
"max": {
"field": "year"
}
},
"min_year": {
"min": {
"field": "year"
}
}
}
}
}
}
# 根据目的地将航班进行分组
GET kibana_sample_data_flights/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"flight_dest": {
"terms": {
"field": "DestCountry",
"size": 10
}
}
}
}
# 根据目的地将航班进行分组,且在组内输出票价
GET kibana_sample_data_flights/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"flight_dest": {
"terms": {
"field": "DestCountry",
"size": 10
},
"aggs": {
"avg_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "AvgTicketPrice"
}
},
"max_price": {
"max": {
"field": "AvgTicketPrice"
}
},
"min_price": {
"min": {
"field": "AvgTicketPrice"
}
}
}
}
}
}
# 根据目的地将航班进行分桶,再根据目的地天气进行分桶,输出每个组内平均票价的统计值
GET kibana_sample_data_flights/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"flight_dest": {
"terms":{
"field": "DestCountry"
},
"aggs": {
# stats 是 Metric 聚合
"stats_price": {
"stats": {
"field": "AvgTicketPrice"
}
},
"weather": {
"terms": {
"field": "DestWeather",
"size": 10
}
}
}
}
}
}
Term 查询
- Term Query / Range Query / Exists Query / Prefix Query / Wildcard Query
Term 是表达语意的最小单位。搜索和利用统计语言模型进行自然语言处理都需要处理 Term。 Term 查询不做分词,会将输入作为一个整体,在倒排索引中查找准确的词项,并且利用相关度算分公式为每个包含该词的文档进行相关度算分。
ES 默认为每个 text 字段都新建一个 keyword 字段,可以通过 keyword 进行精确查询。
POST /products/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"productID.keyword": {
"value": "XHDK-A-1293-#fJ3"
}
}
}
}
- 通过
constant_score可以跳过算分步骤
全文查询
-
Match Query / Match Phrase Query / Query string Query
-
搜索时会分词,查询字符串先找到一个合适的分词器,生成一个供查询的词项列表, 然后针对每个词项在倒排索引中进行查询。
-
Match 查询的过程
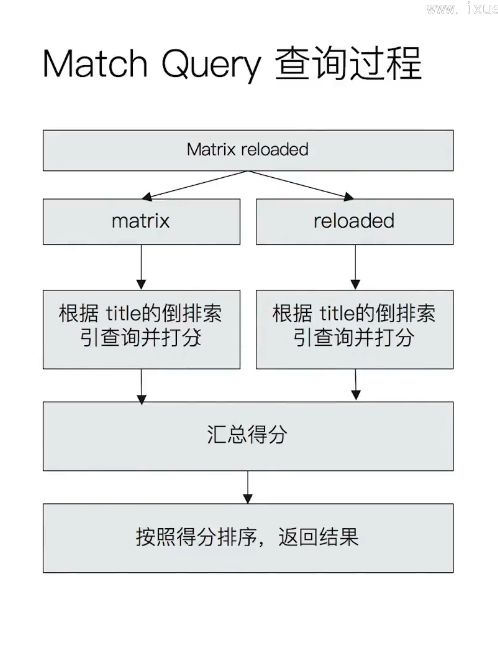
结构化搜索
日期,布尔类型和数字都是结构化的,结构化的数据可以使用 Term 查询。搜索结果只有"是"和"否"两个值。
POST /products/_bulk
{"index": {"_id": 1}}
{"price": 10, "avaliable": true, "date": "2019-01-01", "productID": "XHDK-A-1293-#f13"}
{"index": {"_id": 2}}
{"price": 20, "avaliable": true, "date": "2020-01-01", "productID": "KDKE-A-1293-#f13"}
{"index": {"_id": 3}}
{"price": 30, "avaliable": true, "productID": "JODL-A-9947-#f13"}
{"index": {"_id": 4}}
{"price": 30, "avaliable": false, "productID": "QQPX-R-3956-#f13"}
GET products/_mapping
# 查询某个布尔值字段
POST products/_search
{
"profile": "true",
"explain": true,
"query": {
"term": { "avaliable": true }
}
}
# 跳过算分步骤的布尔查询
POST products/_search
{
"profile": "true",
"explain": true,
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"term": { "avaliable": true }
}
}
}
}
# 数字 Range 查询
GET products/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"price": { "gte": 20, "lte": 30 }
}
}
}
}
}
# 日期 range 查询
# now-1y 表示一年前的今天
GET products/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"range": {
"date": { "gte": "now-1y" }
}
}
}
}
}
# 通过 exists 来处理空值
POST products/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"exists": { "field": "date" }
}
}
}
}
# 处理多值字段,Term 查询是包含,而不是等于
POST /movies/_bulk
{"index": {"_id": 1}}
{"title": "Father of the bridge II", "year": 1995, "genre": "Comedy"}
{"index": {"_id": 2}}
{"title": "Dave", "year": 1993, "genre": ["Comedy", "Romance"]}
GET /movies/_mapping
POST /movies/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"term": { "genre.keyword": "Comedy" }
}
}
}
}
搜索的相关性算分
相关性描述的是搜索语句和文档的匹配程度。ES 5之前,默认的相关性算分采用 TF-IDF,现在采用 BM 25。
- 词频(Term Frequency): 检索词在一篇文档中出现的频率,
检索词出现的次数 / 文档总字数 - DF: 检索词在所有文档中出现的频率
- 逆文档频率(Inverse Document Frequency):
log(全部文档数/检索词出现过的文档总数) - TF-IDF 的本质是将 TF 求和变成了加权求和。
TF(Term1) * IDF(Term1) + TF(Term2) * IDF(Term2) ...
Lucene 中的 TF-IDF 评分公式:
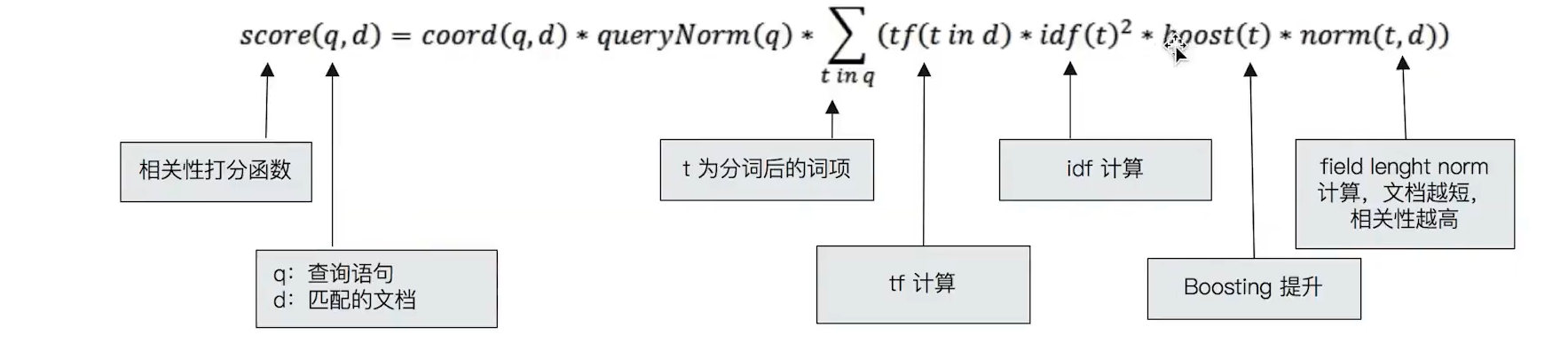
PUT testscore/_bulk
{"index": {"_id": 1}}
{"content": "we use ElasticSearch to power the search"}
{"index": {"_id": 2}}
{"content": "we like ElasticSearch"}
{"index": {"_id": 3}}
{"content": "The scoring of documents is calculated by the scoring formula"}
{"index": {"_id": 4}}
{"content": "you known, for search"}
# 通过打开 explain,可以看到相关性分的计算过程
POST testscore/_search
{
"explain": true,
"query": {
"match": { "content": "elasticsearch" }
}
}
# 通过 Boosting 控制相关度
# boost > 1 时,打分的相关度相对性提升
# 0 < boost < 1 时,打分的权重相对性降低
# boost < 0 时,贡献负分
# 这里的 negative_boost 就是匹配 "like" term 的文档的相关性分会在最后乘 0.2
POST testscore/_search
{
"explain": true,
"query": {
"boosting": {
"positive": {
"term": { "content": "elasticsearch" }
},
"negative": {
"term": { "content": "like" }
},
"negative_boost": 0.2
}
}
}
多字符串多字段查询
在 ES 中,有 Query 和 Filter 两种不同的 Context:
- Query Context: 相关性算分
- Filter Context: 不需要算法(Yes or No),可以利用 Cache,获得更好的性能
布尔查询
布尔查询是一个或多个查询子句的组合。
相关性并不是全文本检索的独有特性,也适用于 Yes | No 的子句,匹配的子句越多,相关性越高。如果多条查询语句被合并成一条复合查询语句,例如 bool 查询,则每个查询子句计算出的评分会被合并到总的相关性评分中。
| 子句 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| must | 必须匹配,贡献算分 |
| should | 选择性匹配,贡献算分 |
| must_not | Filter Context,查询子句,必须不能匹配 |
| filter | Filter Context,必须匹配,但不贡献算分 |
POST /products/_bulk
{"index": {"_id": 1}}
{"price": 10, "avaliable": true, "date": "2019-01-01", "productID": "XHDK-A-1293-#f13"}
{"index": {"_id": 2}}
{"price": 20, "avaliable": true, "date": "2020-01-01", "productID": "KDKE-A-1293-#f13"}
{"index": {"_id": 3}}
{"price": 30, "avaliable": true, "productID": "JODL-A-9947-#f13"}
{"index": {"_id": 4}}
{"price": 30, "avaliable": false, "productID": "QQPX-R-3956-#f13"}
# 布尔查询示例,多个条件之间是 and 的关系。
# 每个子句算的分会汇总起来,变成布尔语句的分
POST /products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"term": {"price": "30"}
},
"filter": {
"term": {"avaliable": true}
},
"must_not": [
{"range": { "price": {"lte": 10} }}
],
"should": [
{"term": {"productID.keyword": "JODL-A-9947-#f13"}},
{"term": {"productID.keyword": "XHDK-A-1293-#f13"}}
]
}
}
}
# filter 和 must_not 都是 Filter Context,不会进行相关性算分,可以看到算出的分都是0
POST /products/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"term": {"avaliable": true}
},
"must_not": [
{"range": {"price": {"lte": 10}}}
]
}
}
}
POST /blogs/_bulk
{"index": {"_id": 1}}
{"title": "Apple iPad", "content": "Apple iPad,Apple iPad"}
{"index": {"_id": 2}}
{"title": "Apple iPad,Apple iPad", "content": "Apple iPad"}
# 通过 boost 控制字段的分数,调整字段之间的优先级
# 当 title 的 boost 较大时,title 长的文档(2)就会排在前面,反之同理
POST /blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"title":{
"query": "apple,ipad",
"boost": 3
}}
},
{
"match": {
"content":{
"query": "apple,ipad",
"boost": 2
}}
}
]
}
}
}
POST /news/_bulk
{"index": {"_id": 1}}
{"content": "Apple Mac"}
{"index": {"_id": 2}}
{"content": "Apple iPad"}
{"index": {"_id": 3}}
{"content": "Apple employee like Apple Pie and Apple Juice"}
# 查询结果中包含了食物信息(3),我们并不想要这一条
POST /news/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {"content": "apple"}
}
}
}
}
# 通过布尔查询将 3 去掉
# 布尔查询多个子句之间是 and 的关系
POST /news/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {"content": "apple"}
},
"must_not": {
"match": {"content": "pie"}
}
}
}
}
# 通过 boosting 降低3的权重,让它排到后面
POST /news/_search
{
"query": {
"boosting": {
"positive": {
"match": {"content": "apple"}
},
"negative": {
"match": {"content": "pie"}
},
"negative_boost": 0.5
}
}
}
单字符串多字段查询
场景归纳
最佳字段 (Best Fields)
当字段之间相互竞争,又相互管理。例如 title 和 body 这样的字段
多数字段 (Most fields)
处理英文内容是:一种常见的手段是,在主字段( English Analyzer)上抽取词干,加入同义词,以匹配更多的文档。相同的文本,加入子字段(Standard Analyzer),以提供更加精确的匹配。其他字段作为匹配文档相关度的信号。匹配字段越多则越好。
DELETE /titles
# 这里有两个字段 title, 和 title.std
PUT /titles
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english",
"fields": {"std": {"type": "text", "analyzer": "standard"}}
}
}
}
}
POST titles/_bulk
{"index":{"_id": 1}}
{"title": "My dog barks"}
{"index":{"_id": 2}}
{"title": "I see a lot of barking dogs on the road"}
# 这里会计算两个字段的分,这样更加符合的文档2就会在前面了
GET titles/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "barking dogs",
"type": "most_fields",
"fields": ["title", "title.std"]
}
}
}
混合字段 (Cross Field)
对于某些实体,例如人名,地址,图书信息。需要在多个字段中确定信息,单个字段只能作为整体的一部分。希望在任何列出的字段中找到尽可能多的词。
# 跨字段搜索
PUT address/_doc/1
{
"street": "5 Poland Street",
"city": "London",
"country": "United Kingdom",
"postcode": "W1V 3DG"
}
# 用一个关键字查询多个字段
POST address/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "Poland Street W1V",
"type": "cross_fields",
"operator": "and",
"fields": ["street", "city", "country", "postcode"]
}
}
}
Disjunction Max Query
将任何与任一查询匹配的文档作为结果返回。采用字段上最匹配的评分作为最终评分返回。
PUT /blogs/_bulk
{"index": {"_id": 1}}
{"title": "Quick brown rabbits", "body": "Brown rabbitq are commonly seen."}
{"index": {"_id": 2}}
{"title": "Keeping pets healthy", "body": "My quick brown fox eats rabbits on a regular basis."}
# 查询算分过程
# 查询 should 语句中的两个查询
# 加和两个查询的评分
# 乘以匹配语句的总数
# 除以所有语句的总数
# 这里的文档1的两个子句的算分平均分更高,所以1在前面
POST /blogs/_search
{
"explain": true,
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{"match": {"title": "Brown fox"}},
{"match": {"body": "Brown fox"}}
]
}
}
}
# 这里使用了 dis_max,返回的最终分数算分是根据最高的那个子句的分数得出的
POST /blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"dis_max": {
"queries": [
{"match": {"title": "Brown fox"}},
{"match": {"body": "Brown fox"}}
]
}
}
}
# 获得评分最高的语句后,tie_breaker 将与其他语句的评分相乘,得到最终评分
POST /blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"dis_max": {
"queries": [
{"match": {"title": "Quick pets"}},
{"match": {"body": "Quick pets"}}
],
"tie_breaker": 0.7
}
}
}
多语言及中文分词与检索
- 使用拼音分词器进行分词
PUT /artists/
{
"settings": {
"analysis": {
"analyzer": {
"user_name_analyzer": {
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter": "pinyin_first_letter_and_full_pinyin_filter"
}
},
"filter": {
"pinyin_first_letter_and_full_pinyin_filter": {
"type": "pinyin",
"keep_first_letter": true,
"keep_full_pinyin": false,
"keep_none_chinese": true,
"keep_original": false,
"limit_first_letter_length": 16,
"lowercase": true,
"trim_whitespace": true,
"keep_none_chinese_in_first_letter": true
}
}
}
}
}
GET /artists/_analyze
{
"text": ["刘德华 张学友 郭富城 黎明 四大天王"],
"analyzer": "user_name_analyzer"
}
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "ldh",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "zxy",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "gfc",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "lm",
"start_offset" : 12,
"end_offset" : 14,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "sdtw",
"start_offset" : 15,
"end_offset" : 19,
"type" : "word",
"position" : 4
}
]
}
使用 Search-Template 和 Index-Alias 查询
Search Template 可以定义一个查询,将 查询优化 和 使用查询 这两个工作分开, SearchTemplate 的语法参考官方文档。
# 定义搜索模板,通过 POST 也可以更新这个模板
POST _scripts/tmdb
{
"script": {
"lang": "mustache",
"source": {
"_source": [
"title", "overview"
]
},
"size": 20,
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "{{q}}",
"fields": ["title", "overview"]
}
}
}
}
# 使用搜索模板
POST tmdb/_search/template
{
"id": "tmdb",
"params": {
"q": "basketball with cartoon aliens"
}
}
Index Alias,为索引创建一个别名,可以实现0停机运维。
# 为索引创建一个别名,可以将 tmdb-latest 当做 tmdb 来使用
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "tmdb",
"alias": "tmdb-latest"
}
}
]
}
# 为索引创建别名,同时附带过滤条件,tmdb-latest-highrate 这个索引和 tmdb 索引的结构一样,但是只有 2191 个结果。(tmdb 有 3051 个结果)
POST _aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "tmdb",
"alias": "tmdb-latest-highrate",
"filter": { "range": { "vote_average": { "gte": 6 } } }
}
}
]
}
利用 Function-Score-Query 优化算法
PUT /blogs/_doc/1
{
"title": "About popularity",
"content": "In this post we will talk about...",
"votes": 0
}
PUT /blogs/_doc/2
{
"title": "About popularity",
"content": "In this post we will talk about...",
"votes": 100
}
PUT /blogs/_doc/3
{
"title": "About popularity",
"content": "In this post we will talk about...",
"votes": 1000000
}
# 设置新的相关度分 = 旧相关度分数 * votes
POST /blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "popularity",
"fields": ["title", "content"]
}
},
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "votes"
}
}
}
}
# 对排序结果进行随机排序
POST /blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"random_score": {
"seed": 234
}
}
}
}
Term&Phrase Suggester
Term Suggester
POST articles/_bulk
{ "index": {} }
{ "body": "lucene is very cool" }
{ "index": {} }
{ "body": "Elasticsearch builds on top of lucene" }
{ "index": {} }
{ "body": "Elasticsearch rocks" }
{ "index": {} }
{ "body": "elastic is the company behind ELK stack" }
{ "index": {} }
{ "body": "Elk stack rocks" }
{ "index": {} }
{ "body": "elasticsearch is rock solid" }
# 针对 lucen 会返回一个正确的推荐
# 推荐的两种模式
# 1. missing,如果关键字没有查询到,那么就返回已有 Token 索引的推荐
# 2. Popular,返回索引 Token 出现频率更高的词
POST /articles/_search
{
"size": 1,
"suggest": {
"term-suggestion": {
"text": "lucen hocks",
"term": {
"prefix_length": 0,
"suggest_mode": "popular",
"field": "body"
}
}
}
}
Phrase Suggester
POST /articles/_search
{
"suggest": {
"my-suggestion": {
"text": "lucne and elasticsear rock hello world",
"phrase": {
"field": "body",
"max_errors": 2,
"confidence": 2,
"direct_generator": [{
"field": "body",
"suggest_mode": "always"
}],
"highlight": {
"pre_tag": "<em>",
"post_tag": "</em>"
}
}
}
}
}
## 返回结果
"suggest" : {
"my-suggestion" : [
{
"text" : "lucne and elasticsear rock hello world",
"offset" : 0,
"length" : 38,
"options" : [
{
"text" : "lucene and elasticsearch rock hello world",
"highlighted" : "<em>lucene</em> and <em>elasticsearch</em> rock hello world",
"score" : 1.5788074E-4
}
]
}
]
}