Thrift golang client 如何设置超时时间
简介
本文以 golang thrift binary 协议为例,讲述 thrift golang client 如何设置超时时间
如何设置超时时间
golang thrift client 有两个超时时间
- socket timeout
在创建 TSocket 的时候,我们可以传入 ConnectTimeout 和 SocketTimeout 两个配置。
ConnectTimeout表示建立 TCP 连接的超时时间SocketTimeout表示读写 Socket fd 时的超时时间
当这两个超时触发时,thrift 会返回一个 err.Timeout() == true 的 error, 表示超时错误,thrift 会将其包装成 TTransportException,其 typeId == thrift.TIMED_OUT
rawTransport := thrift.NewTSocketConf(net.JoinHostPort("localhost", "7303"), &thrift.TConfiguration{
SocketTimeout: 5 * time.Second,
ConnectTimeout: 5 * time.Second,
})
- context timeout
在调用 thrift 函数时,需要传入 context 参数,我们可以在 ctx 参数中加上超时
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 1 * time.Second)
res, err = client.Triple(ctx, 27) // thrift 调用
cancel()
根据 context 的工作原理,
cancel函数被调用- 到了设置的超时时间,golang context 内部的的 goroutine 会调用 cancel 函数
当上述两个条件满足其一时,会触发两个函数
ctx.Done()返回的 channel 会 closectx.Error() != nil
设置超时时间的注意事项
- socket timeout 必须比 context timeout 小
- 在弱网环境下,不能将 socket timeout 设置的非常小, context timeout 设置的特别大
- 遇到超时错误后应该将连接关闭
为什么要遵循这些规则,我们先了解 timeout 工作原理,最后再来解答。
超时时间是如何工作的
为了了解这两个超时时间是如何工作的,我们首先需要理清楚 binary protocol 中函数的调用关系
binary protocol 中的函数调用关系
在 lib/go/thrift/protocol.go 函数中,实现了 TProtocol 接口,此接口中定义了若干 ReadXXX 函数,这些函数负责从 Transport 中读取 thrift 请求体和响应体。
type TProtocol interface {
// 若干 Write 函数
ReadMessageBegin(ctx context.Context) (name string, typeId TMessageType, seqid int32, err error)
ReadMessageEnd(ctx context.Context) error
ReadStructBegin(ctx context.Context) (name string, err error)
ReadStructEnd(ctx context.Context) error
ReadFieldBegin(ctx context.Context) (name string, typeId TType, id int16, err error)
ReadFieldEnd(ctx context.Context) error
ReadMapBegin(ctx context.Context) (keyType TType, valueType TType, size int, err error)
ReadMapEnd(ctx context.Context) error
ReadListBegin(ctx context.Context) (elemType TType, size int, err error)
ReadListEnd(ctx context.Context) error
ReadSetBegin(ctx context.Context) (elemType TType, size int, err error)
ReadSetEnd(ctx context.Context) error
ReadBool(ctx context.Context) (value bool, err error)
ReadByte(ctx context.Context) (value int8, err error)
ReadI16(ctx context.Context) (value int16, err error)
ReadI32(ctx context.Context) (value int32, err error)
ReadI64(ctx context.Context) (value int64, err error)
ReadDouble(ctx context.Context) (value float64, err error)
ReadString(ctx context.Context) (value string, err error)
ReadBinary(ctx context.Context) (value []byte, err error)
ReadUUID(ctx context.Context) (value Tuuid, err error)
// ...
}
lib/go/thrift/binary_protocol.go 文件提供了 TProtocol 的一种实现,它用于读取 binary 协议格式的 thrift 请求/响应。
其中, ReadXXX 函数的调用关系如下:
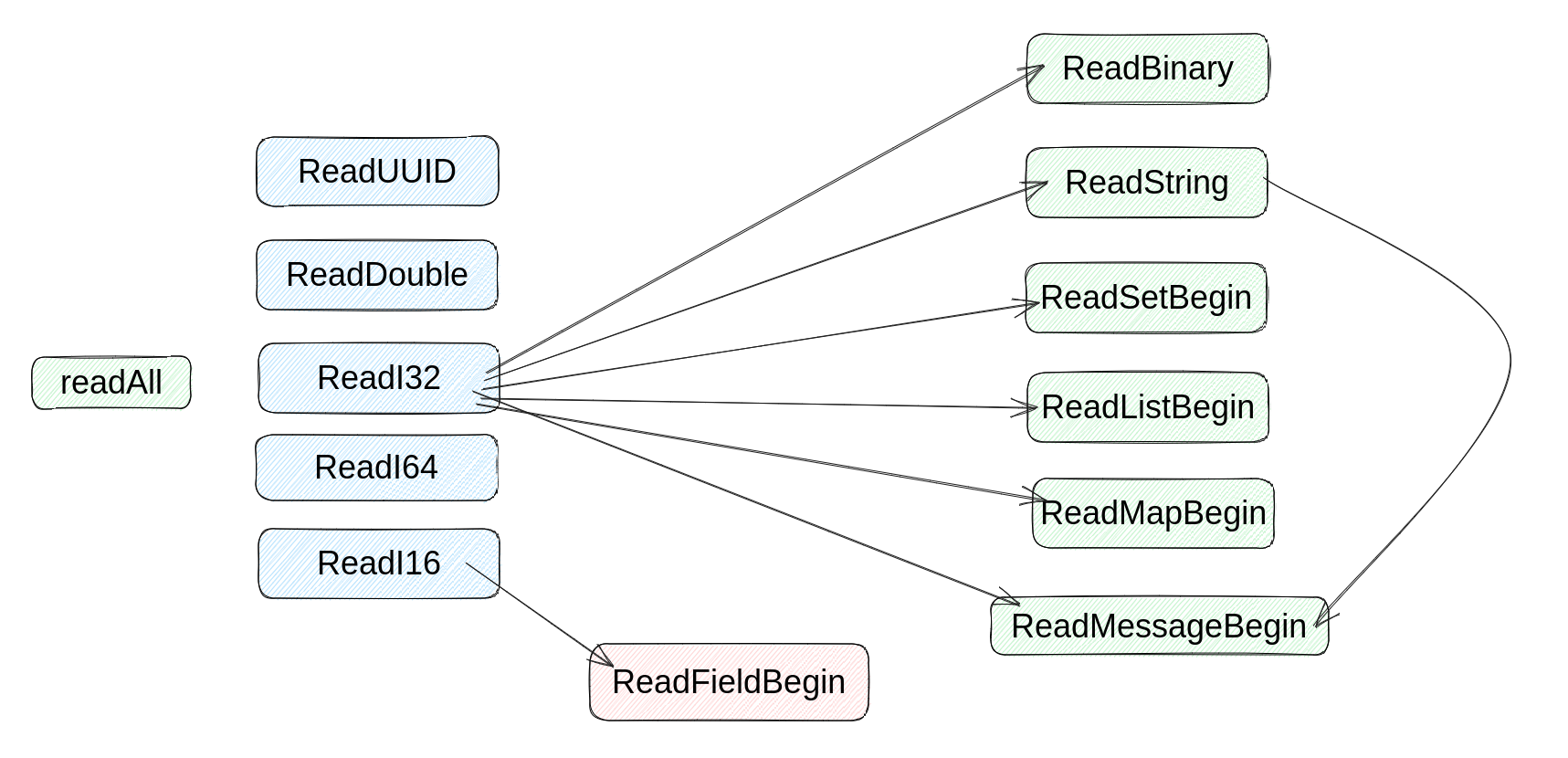
可以看到,除了若干以 End 结尾的函数,和 ReadByte, ReadBool 之外,所有的 Read 函数都调用了 readAll 函数。
而关于 thrift 超时时间的玄机就隐藏在 readAll 函数中
readAll 函数中如何检查超时
这是 readAll 函数的代码,
read, err = io.ReadFull(p.trans, buf) 表示从 protocol 底层的 transport 读取数据,读完之后进行一个复杂的 if 条件判断,决定重试还是返回错误。
_, deadlineSet := ctx.Deadline()
for {
read, err = io.ReadFull(p.trans, buf)
if deadlineSet && read == 0 && isTimeoutError(err) && ctx.Err() == nil {
// This is I/O timeout without anything read,
// and we still have time left, keep retrying.
continue
}
// For anything else, don't retry
break
}
return NewTProtocolException(err)
它的 if 条件有四个子条件
- ctx 设置了 deadline, 即 ctx 用
WithTimeout,WithDeadline包裹了 - protocol 底层的 transport 中读取的数据为0
- protocol 底层的 transport 读取时返回的 err 是 timeout error
- ctx 的 cancel 函数没有被调用(这也表示 WithTimeout ctx 没有超时),
ctx.Err() == nil
当四个条件都满足时,它会重新重试,重新从 tranport 中读取数据,否则会将错误返回。
至此,我们可以将 thrift 客户端的超时逻辑梳理清楚了,protocol 通过 transport 去读取数据,当它遇到了 timeout error,但没有读到数据且 ctx 设置的超时时间未到,会重试继续读数据。否则就会返回超时错误。
我们可以用下面这张图来表示

- step1 表示从 client 开始调用到 socket fd 返回第一个字节经过的时间
- step2 表示从 client 开始接受第一个字节,到接受整个请求所花费的时间
- 在 step1 中,client 遇到 socket timeout 会进行重试,直到到达了 ctx 设置的时间上限
- 在 step2 中,client 遇到 socket timeout ,大多数时候都是直接返回 timeout error, 只有 特别极端的案例 ,才会进行重试。
特别极端的案例是什么:
假设有这样的响应,
- socket fd 首先发会了 thrift message header,
- 正好发完 message header 之后, 网络阻塞了
- 此时 client 正在调用
ReadFieldBegin函数读取参数结构体,它遇到 socket timeout error 就会进行重试
在 golang server 中,响应是一起发送的,所以不存在 server 主动卡住的请求,TCP 发送字节的情况特别随机,几乎不可能存在正好发送完 message header 就卡住的情况(而且 message header 长度还是可变的),所以可以认为这种特别极端的情况不存在。
回到注意事项
了解完实现细节后,我们再来看文章开头提到的两个注意事项
- socket timeout 必须比 context timeout 小
在上文的 readAll 函数中,当 socket timeout 触发时,会检查是否达到了 context timeout 的限制,如果我们设置了 socket timeout > context timeout, 那么就会存在 context timeout 到了限制时间,但函数仍然阻塞在 transport.Read 中的情况
- 弱网环境中,socket timeout 不能设置的特别小
在上一节的分析中,我们知道了在 step2 中遇到了 socket timeout时, 请求会直接失败,返回 timeout error。
那么在弱网环境中,如果我们将 socket timeout 设置的很小,但是 context timeout 很大,那么会遇到很多在 step2 中因为 socket timeout 导致的超时错误,而 context timeout 实际上还远远达不到。
- 遇到超时错误后,应该将连接关闭
如果遇到超时错误了,client 会直接返回错误,但是过了一段时间 server 又将响应发回来了,后续的 新请求 就可能读到 旧响应 。
此时因为 thrift 请求和响应的 seq_id 或 method name 对不上,就会返回错误
{method_name}: out of order sequence response // seq id 对不上
{method_name}: wrong method name // 方法名对不上
这部分检查代码在 lib/go/thrift/client.go:56 文件的 func (p *TStandardClient) Recv 函数中
func (p *TStandardClient) Recv(ctx context.Context, iprot TProtocol, seqId int32, method string, result TStruct) error {
rMethod, rTypeId, rSeqId, err := iprot.ReadMessageBegin(ctx)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if method != rMethod {
return NewTApplicationException(WRONG_METHOD_NAME, fmt.Sprintf("%s: wrong method name", method))
} else if seqId != rSeqId {
return NewTApplicationException(BAD_SEQUENCE_ID, fmt.Sprintf("%s: out of order sequence response", method))
...